What kind of planet is Mars? Properties of the planet Mars, its mass, temperature, distance from the Sun. Information about the planet Mars.
Source : pixabay.com
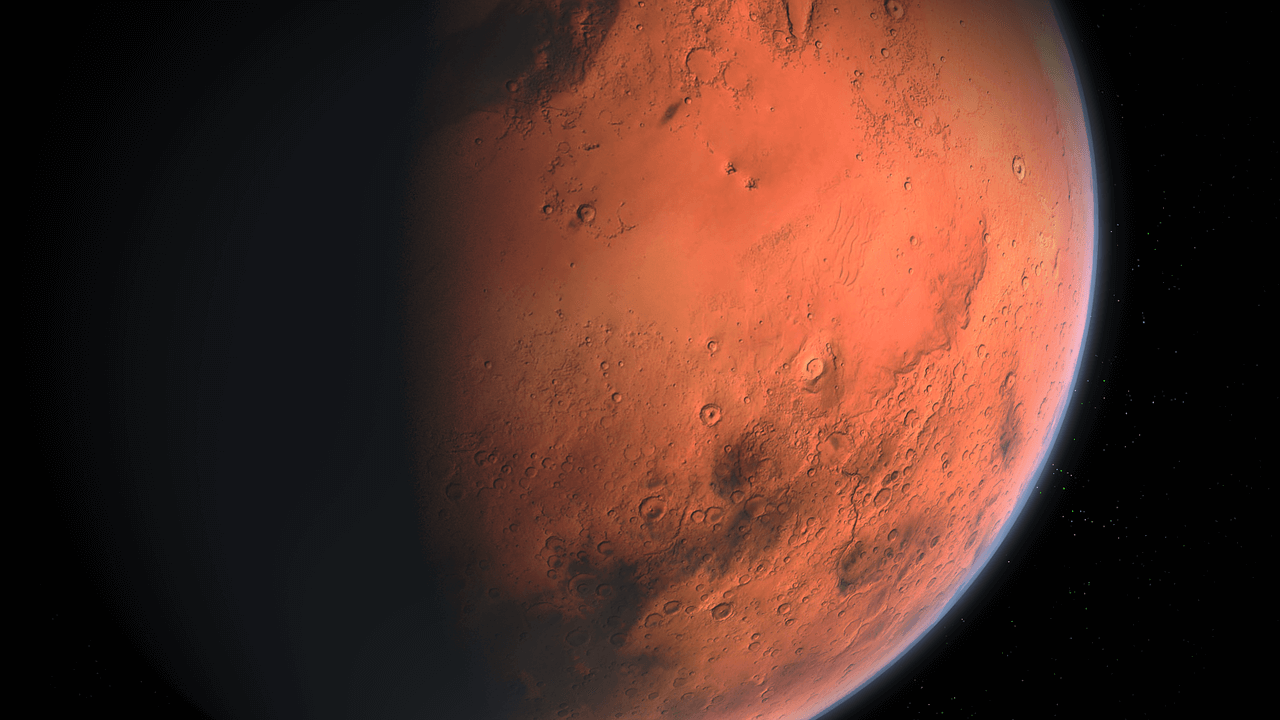
Mars is a planet that is part of our solar system, it is the fourth planet counting from the sun; it is counted within the set of the so-called interior or telluric planets. Its size is close to a third of that of the earth, it can be seen with the naked eye easily identified both by its apparent brightness and by its reddish-orange coloration.
The planets of this set are called telluric because they are formed mainly of siliceous materials and other minerals such as metals and basalts. They are also referred to as interiors because they are inside the zone delimited by the asteroid belt, which is taken as a reference point to separate them from the gaseous planets, which are located outside of the zone, such as Jupiter or Saturn.
The name of this planet is due to the fact that the Greeks identified this planet, with the god of war Ares, this belief being assimilated by the Romans, naming it with the Roman version of the name of the god of war (Mars), name that spread more, being the name with which it is known until today.
Characteristics of the Planet Mars:
Description
Mars is a celestial body belonging to the so-called planets; it is a celestial body that does not have its own light, but reflects the light coming from the sun, which is apparently a reddish-yellowish color from the ground, although according to recent research it is more of a brown-orange tone, thanks to that the surface of Mars contains a lot of iron, which gives it that color.

Source : pixabay.com
Shape
It is rounded, slightly flattened in the south and north poles, having a polar diameter of 6,750 km and in the equator of 6,794 km.
Rotation
It has a rotation that lasts 24:64 hours, being longer than the earth for almost an hour, the day and night lasts approximately twelve and a half hours and the Martian year (the movement around the sun) is 687 Earth days, exceeding the Earth year in just over 22 days.
Formation
It was formed of siliceous materials, basalts and other minerals such as metals, making the density of the planet superior to that of some outer planets such as Neptune.
Size
It is a planet that has a smaller size than the earth, (having approximately one third of its size), but whose surface being devoid of seas has an extension equivalent to the land emerged on our planet.
Mass
By having a mass lower than that of the earth, its gravity is much lower than that of the earth, being 3,711 m / s², (the gravity of the earth is 9.78 m / s²), and comparing it with the The gravity of the moon (1,622 m / s²) is greater.

Source : pixabay.com
Atmosphere
Mars has a very light atmosphere compared to that of the earth, which protects the planet less from impacts of meteorites of sizes that its counterpart of the Earth can disintegrate. Its atmosphere consists mainly of carbon dioxide, nitrogen, and argon, although water and methane have also been identified in it.
There are suspended dust particles, iron being a large part of it, which gives it that reddish-brown color, just like the surface of the planet. Its atmosphere has a much lower pressure than the earth, being one of the reasons why it is difficult to find liquid water on its surface, combined with the high and low temperatures that occur on the surface of the planet, which they cause the freezing and immediate evaporation (sublimation) of the water on the surface.
Surface
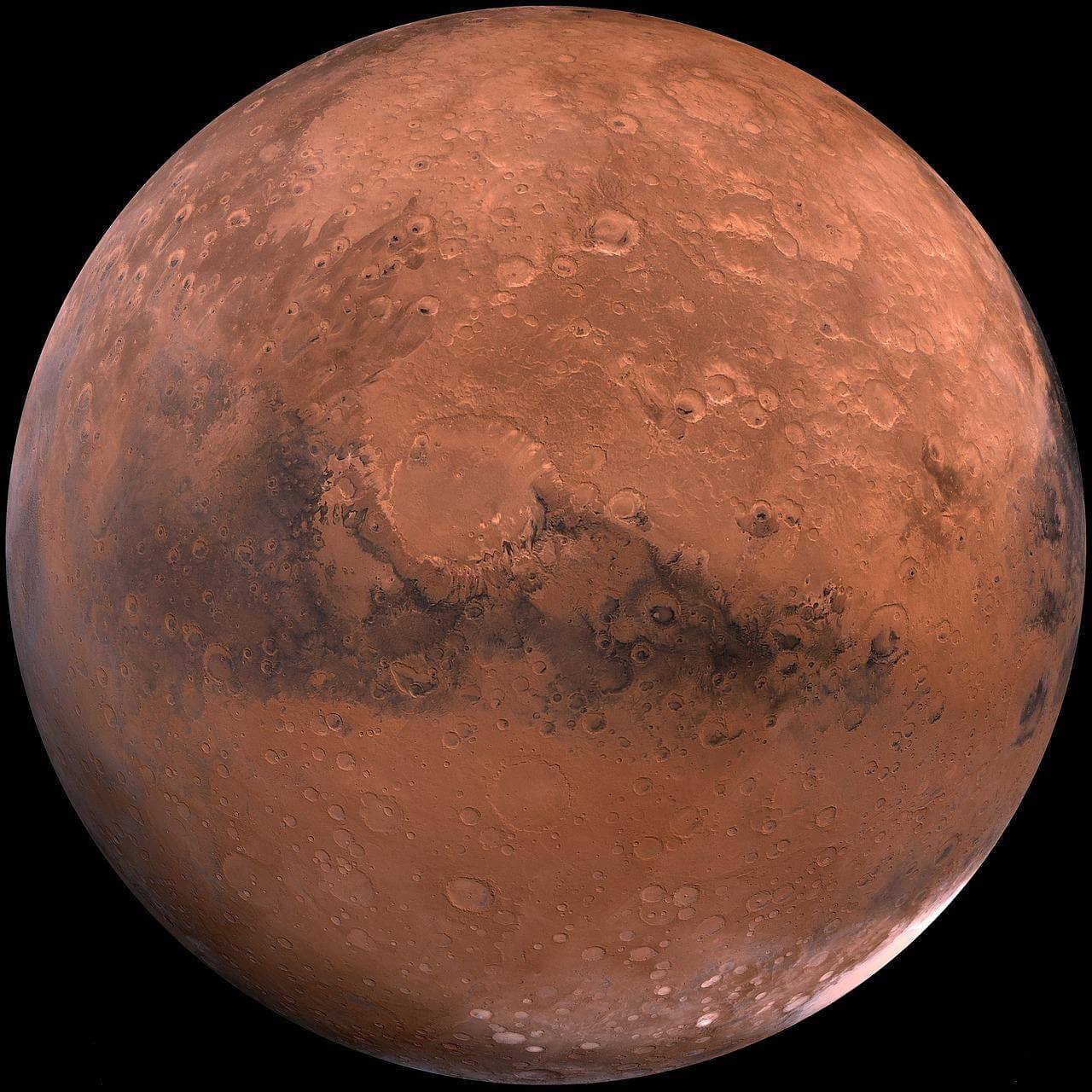
The Martian surface presents testimonies of the geological changes that have taken place over millennia, such as valleys and mountain chains resulting from volcanic activity. Among its mountains is Mount Olympus, which has a height of 24 kilometers and is the volcano with the highest known height.
There are large canyons that have possibly been formed by causes such as the opening of cracks in the surface, produced by volcanic activity, the impact of meteorites or the existence of waterways in ancient times.
Likewise, it presents numerous craters products of impacts of meteorites of various sizes, reaching craters as large as the “Borealis” crater, which covers almost forty percent of the Martian surface.
Poles
At its poles there are large areas of ice, mainly carbon dioxide ice, although water ice has also been found.
Magnetic field
At present, the planet does not have a global magnetic field, which protects it from the cosmic rays and from the different radiations coming from the sun; however, there have been indications of the existence of intensely magnetized regions, which are apparently vestiges of the magnetic field that he owned a long time ago.
Life
The absence of a global magnetic field, extreme temperatures, the relatively weak atmosphere, the current lack of water in a liquid state, and other factors, make one think that the planet does not harbor life.
Hypothesis
There are hypotheses concerning the fact that at some previous geological moment, it could harbor some type of primitive life of the microbial type, and even that it could exist at present in its extreme conditions. This is thought thanks to the fact that living beings have been found on Earth in conditions similar to those of Mars, such as in the depths of caves and simas, as well as in underwater regions where sunlight does not reach, or in volcanic regions and regions such as Antarctica where live bacteria have been found in places with high temperatures and below -80 ° C. Although the current investigations have not been able to verify or deny these hypotheses.