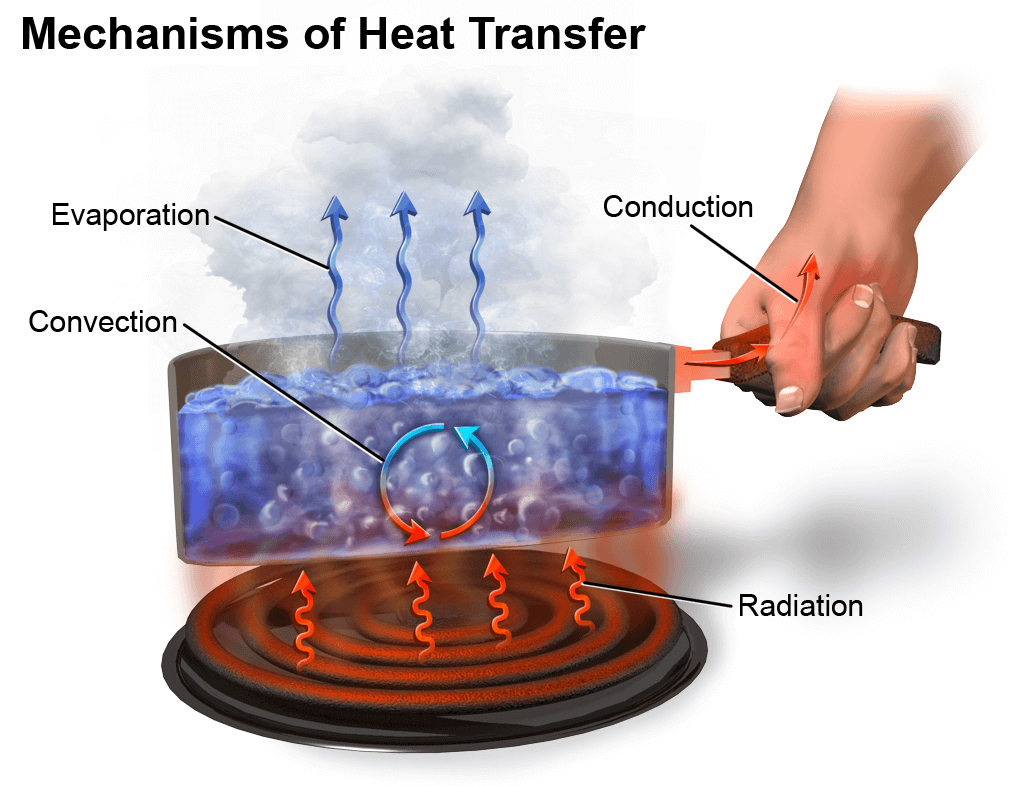
What is radiation? How does the heat transfer occur by radiation? What are the heat transfer methods and information?
The sun is our main source of heat, light, and most other forms of energy. But the transfer of heat from the sun to the earth cannot be explained by either method that you have studied so far. In both conduction and convection, heat is transferred by the molecules of some material. The atmosphere extends about 500 miles above the earth’s surface. Beyond the atmosphere the rest of the 93 million miles to the sun is space. And in space, the molecules are very far apart. Yet you know that in some way the earth does get heat from the sun. So there must be some method of heat transfer without molecules.
Scientists have discovered that energy from the sun reaches the earth in the form known as radiant energy. This form of energy can leave the material from which it comes and shoot through space or through air. It travels at a tremendous speed of 186,000 miles a second. This is the same as the speed of light, which is just the variety of radiant energy that we can see. Radiant energy moves out in all directions from its source. We say that it radiates, because it spreads out from the center in straight lines, or rays.
Source : en.wikiversity.org
Radiant energy is not heat, but it can be changed into heat. When radiant energy strikes materials that can absorb it, it makes the molecules of the materials move faster. So the radiant energy is changed into heat energy. You have often felt the sun shining through a window on a cold day. The air outdoors was cold, and the window panes were cold. Radiant energy from the sun was passing through the air and the glass without warming them very much. But when the radiant energy struck your clothes and body, it was absorbed and changed into heat, which made you feel warm.
When radiant energy strikes a material, three different things may happen:
- Radiant energy may pass right through.
- It may be reflected.
- It may be absorbed and changed into heat.
Usually, radiant energy is partly reflected and partly absorbed. Transparent materials let much radiant energy pass through. They reflect some and absorb a little of it. Materials with light, shiny surfaces are poor absorbers of radiant energy, because they reflect most of it that strikes them. However, materials that have dark, dull surfaces are good absorbers.
Some people think that the radiant energy which warms them is the light from the sun or a fire. This idea is only partly true. Light is a variety of radiant energy. It can warm things a little when it is absorbed and changed into heat. When we notice heat being transferred by radiation, light is almost always coming from the same source. So we are likely to think that light actually warms us more than it does. But most of the radiant energy that is changed into heat is energy which cannot be seen. It is mostly the variety of radiant energy known to all of us as infrared rays.
Heat moves from warmer things to cooler things.
When there is only air or space between objects heat is transferred by radiation. Almost all objects give out some radiant energy. A hot object gives out much radiant energy, while a cooler object nearby gives out less. Each object receives and absorbs radiant energy from the other, but the cooler object gets more energy than it sends back. Right now, your body is giving out radiant energy. At the same time, the walls of the room are radiating energy back to you. Since the radiant energy is invisible, you usually do not notice it. Yet if the walls ever stopped radiating, you would almost freeze. Your body would keep on radiating its energy, but you would be getting no energy in return. Cool walls in a room let you cool off rapidly even though the air around you is warm.
Now you can understand how transfer of heat by radiation is quite different from transfer of heat by conduction and convection. In radiation, no molecules are needed to transfer the heat. Energy is radiated from the sun or a fire through space or air directly to materials. This energy passes through transparent materials, such as air and glass, without warming them very much. But when the radiant energy is absorbed by a material and changed into heat, the molecules of the material move faster. Then the material feels warmer.