What is the difference between Raman effect and Rayleigh scattering? Scientific explanation of the most fundamental differences between Raman effect and Rayleigh scattering.
The Raman Effect and Rayleigh scattering are two different phenomena that occur when light interacts with matter. Both are important concepts in the field of optics and have a wide range of applications in various scientific and industrial fields. However, they differ in their causes and the manner in which they scatter light.
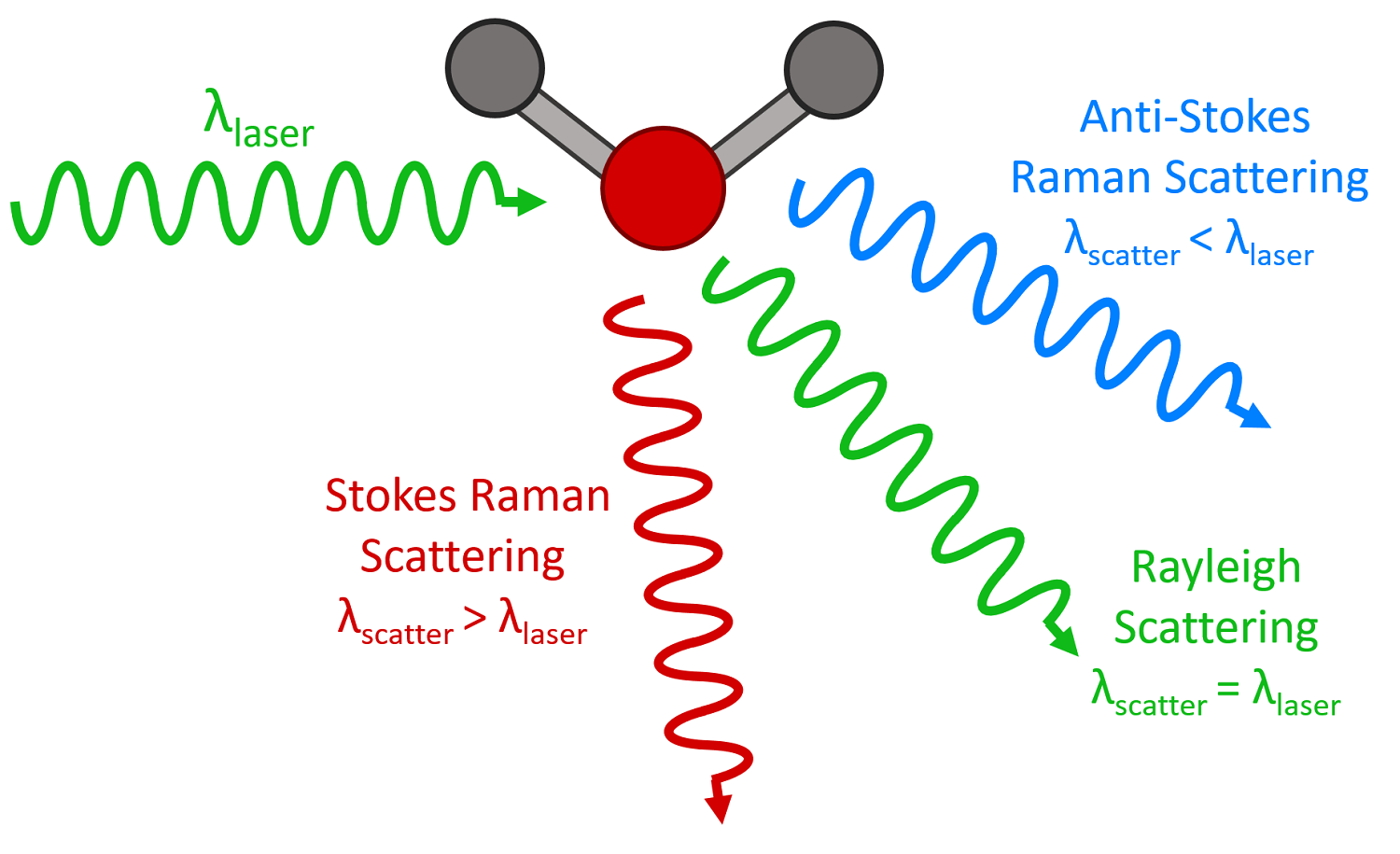
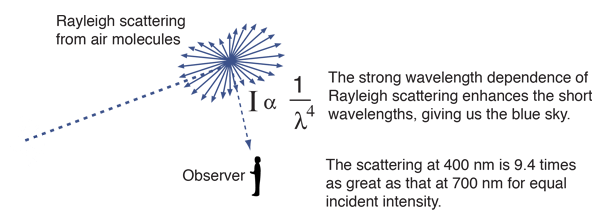
Rayleigh scattering occurs when light scatters due to the interaction with small particles, such as air molecules, that are much smaller than the wavelength of light. When light encounters these small particles, it causes a change in the refractive index of the medium, which results in the scattering of light in all directions. This scattering is known as Rayleigh scattering and it is characterized by the blue color of the sky and the yellow color of the sun at sunrise and sunset.
On the other hand, the Raman Effect occurs when light scatters due to the interaction with the vibrational energy levels of molecules. When light encounters a molecule, it can cause the molecule to change its vibrational energy state, which results in the scattering of light. This scattered light has a different frequency than the incident light and is known as Raman scattered light. The Raman Effect is characterized by the appearance of new spectral lines in the scattered light, which are not present in the incident light.
The main difference between Rayleigh scattering and the Raman Effect is the cause of the scattering. Rayleigh scattering is caused by the interaction of light with small particles, while the Raman Effect is caused by the interaction of light with the vibrational energy levels of molecules. Another difference is that Rayleigh scattering is characterized by a relatively small shift in the frequency of the scattered light, while the Raman Effect is characterized by a relatively large shift in the frequency of the scattered light.
In terms of applications, Rayleigh scattering is primarily used to study the atmospheric properties of the Earth and the distribution of aerosols in the atmosphere. On the other hand, the Raman Effect is widely used in various scientific and industrial applications, such as chemical analysis, mineral identification, and medical diagnosis. The Raman Effect is also used to study the molecular structure of materials, to determine the composition of materials, and to study the properties of liquids and gases.
In conclusion, both Rayleigh scattering and the Raman Effect are important phenomena that occur when light interacts with matter. While they have similarities, such as the scattering of light in all directions, they differ in their causes and the manner in which they scatter light. Rayleigh scattering is caused by the interaction of light with small particles, while the Raman Effect is caused by the interaction of light with the vibrational energy levels of molecules. Both have a wide range of applications in various scientific and industrial fields and are essential concepts in the field of optics.