Where is the Sea of Azov? Our page with general information about the Azov sea map and the geographical features of the Azov sea.

Sea of Azov (Source : pixabay.com)
Azov Sea, Russian azovskoye or azovskoe more, also known as the Sea of Azov. Inland sea connected to the Atlantic Basin. It is located in the south of the European territory of Russia and on the southeast coast of Ukraine. Its area is approximately 38,000 square kilometers and its deepest point is 14 meters. It is the shallowest sea in the world. It receives the waters of the large Don and Kuban rivers and small rivers such as Mius, Berda, Obitochnaya and Yeya. It is connected to the Black Sea, from which it is separated by the Kerch and Taman peninsulas, by the Kerch Strait. The Azov Sea has a geological history that is closely tied to the Black Sea. After forming as part of a large basin in the Middle Miocene Section (16 million years ago), it broke away from the ocean together with the Black Sea Basin in the Lower Pliocene (7 million years ago). In the following period, Azov joined and separated many times with the Caspian Sea, at the beginning of the Fourth (Quaternary) Period (c. 5 million years ago) roughly took its present form. The connection between the Black Sea and the Mediterranean (the layer known as the Karangats Basin) was formed towards the end of this period.
A temperate continental climate dominates the Sea of Azov. In winter, winds blowing from the northeast and east bring cold air from the mainland. Under the influence of cyclones, frost and thaw events follow each other; fog is common. July is the hottest month.
The water pattern of the Azov Sea is determined by the terrestrial location, climate, waters coming from the rivers, water exchange with the Black Sea and water-based activities carried out in the basin . Average salinity is generally low due to the abundance of fresh water. However, depending on the changes in the water exchange in the Kerch Strait and the flow of the rivers, the salinity can be seen from the difference according to the years. Especially in Sivas Lake, the salt rate is high.
In the Sea of Azov, currents are only counterclockwise, but sometimes they can turn in the opposite direction under the influence of the wind. Depending on the water coming from the rivers, the average water level, which varies by 33 cm from year to year, can rise by about 5.5 meters with the tidal movement.
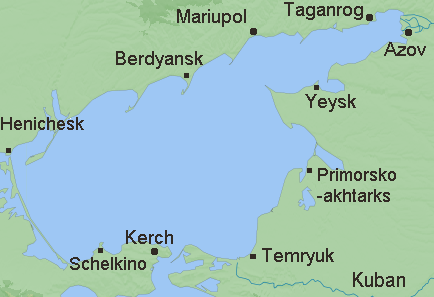
Azov Sea Cities (Source : wikipedia.org)
Biological productivity was very high because the sea was shallow, the water was mixed and heated evenly, and the water from the rivers contained large amounts of nutrients. Only in the summer, during long periods of stagnation, the complete dissipation of oxygen at the bottom by oxidation could lead to the death of the fish. But today, it is reported that almost all life in the Azov Sea has come to an end due to the toxic waste carried by the rivers.
The Sea of Azov transports a large amount of goods and passengers, although heavy ocean-going vessels cannot pass through some very shallow areas. In winter, sea voyages are made with the help of icebreakers. Major ports are Taganrog and Yeysk in Russia and Idanov and Berdyansk in Ukraine.