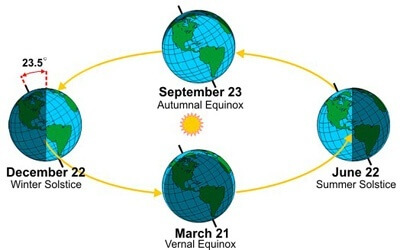
The seasons occur because the Earth’s axis is tilted at an angle of approximately 23.4 degrees and different parts of the Earth receive more solar energy than others.
Due to the axial inclination of the Earth (obliquity), our planet orbits the Sun in an inclination that means that different areas of the Earth point towards or away from the Sun at different times of the year.
 Astronomical terms and definitions
Astronomical terms and definitions
Around the June solstice, the North Pole is tilted towards the Sun and the Northern Hemisphere receives more of the direct rays of the Sun. That is why June, July and August are summer months in the northern hemisphere.
Opposite stations
At the same time, the Southern Hemisphere points towards the Sun, creating winter during the months of June, July and August. Summer in the Southern Hemisphere is in December, January and February, when the South Pole is tilted towards the Sun and the Northern Hemisphere is tilted.
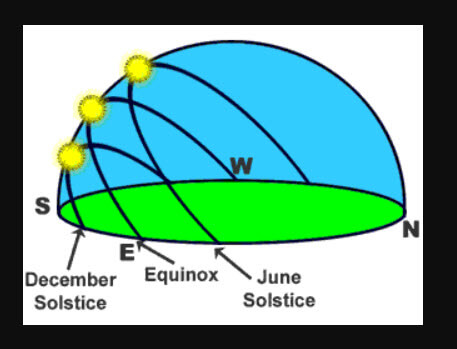
Axis leans in the same way
The direction of the Earth’s inclination is almost unchanged: the two hemispheres point to the same position in space throughout the year. What does change, as the Earth revolves around the Sun, is the position of the hemispheres in relation to the Sun: the northern hemisphere points towards the Sun during the northern summer and away from the Sun during the northern winter.
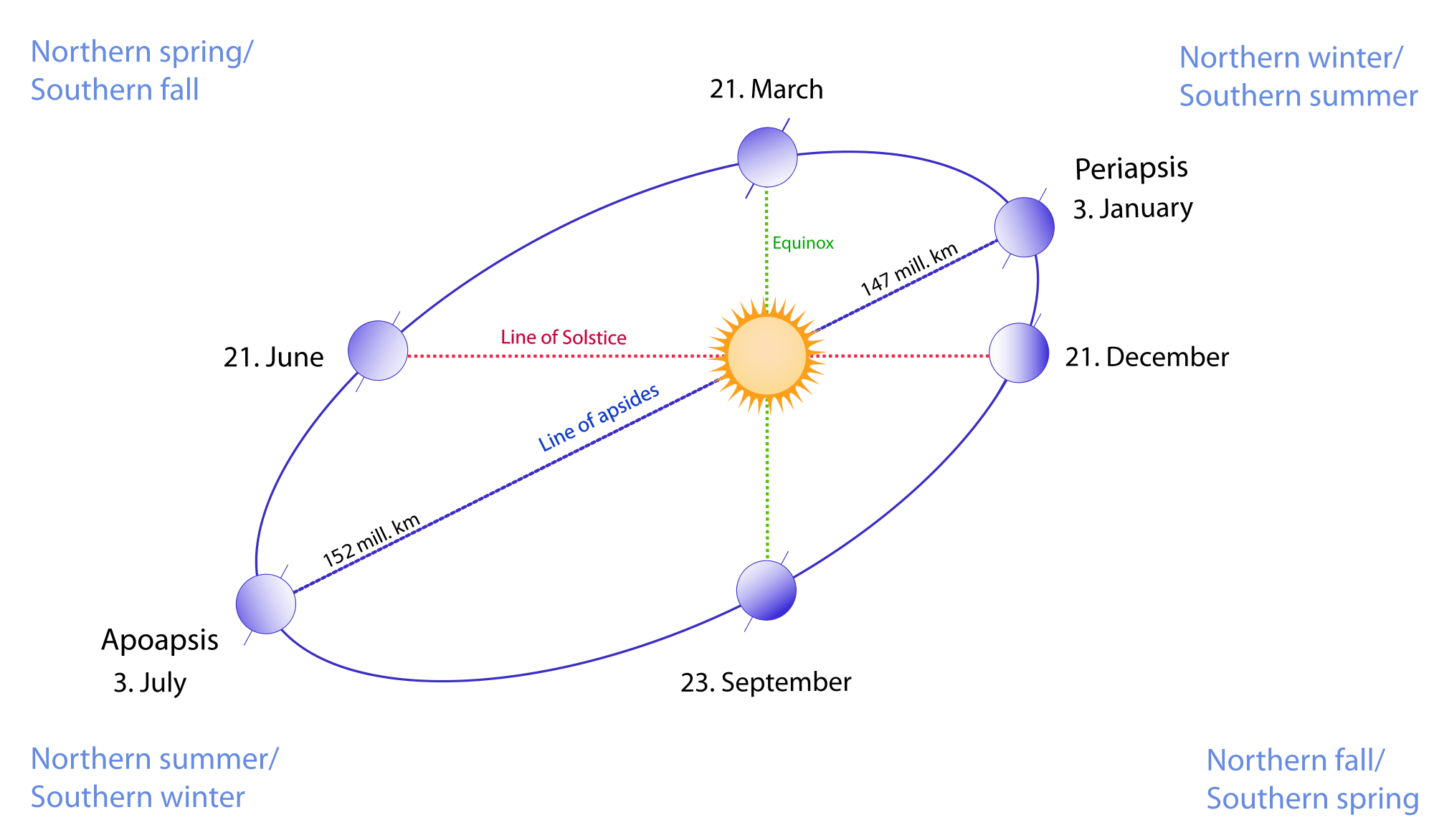
Elliptical path around the sun
The path of the Earth around the Sun is not circular, nor is the Sun at the center of this path. Instead, Earth’s orbit is elliptical, with the Sun closer to one end of the orbital path than the other. This means that the distance from the Earth to the Sun varies throughout the year.
The distance does not cause stations
It is a common misconception that the seasons occur because of the elliptical orbit of the Earth around the Sun, with the winter occurring when the Earth is furthest away from the Sun, and the summer when it is closest to it.
However, the distance from our planet to the Sun has little effect at the beginning of the seasons. In fact, the Earth is closer to the Sun, or in its Perihelion, around the winter solstice of the Northern Hemisphere, while it is farther from the Sun, or in its Afelio, around the northern summer solstice.
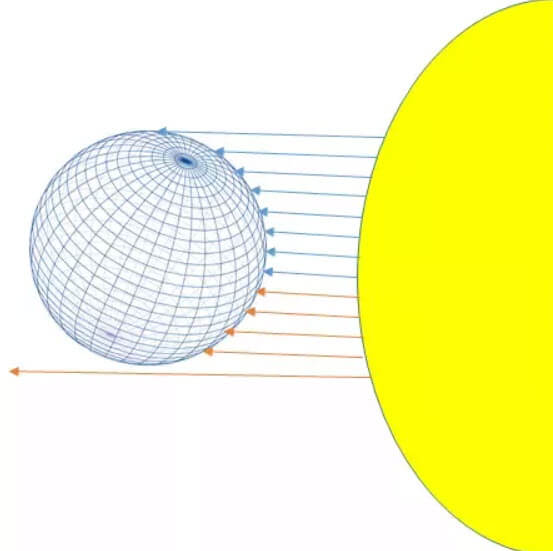
Small difference
Although the variation of the distance of the Earth from the Sun is not very large, our planet receives more solar energy when it is closer to the Sun during the summer of the southern hemisphere. However, because there are relatively few land masses south of the equator and the oceans take longer to warm, the temperature difference between the northern and southern summers is very small.