What are the common features, characteristics of living things (living organisms)? In biology how is the living organism described, the common features.
The branch of science that studies living things is biology. Biology is formed by combining the Greek words bios meaning “life” and logos meaning “science = study”. In order to qualify the assets as living; It is checked whether it has features such as cellular structure, nutrition, respiration, excretion, movement, reaction to stimuli, metabolism, homeostasis, harmony, organization, reproduction, growth and development. Assets that have these characteristics are defined as living, and the state of being alive is defined as vitality. Some of the common features of living things are:
Source: pixabay.com
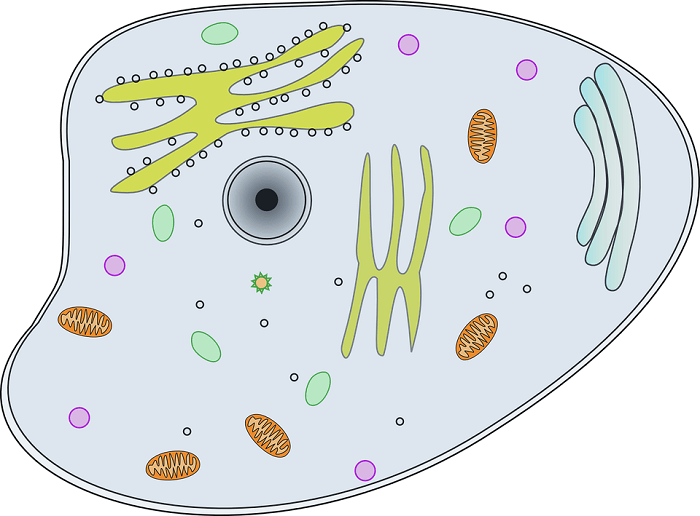
Cellular Structure
- • The structural and functional unit of organisms is the cell.
- • Cells are structurally of two types, prokaryotic and eukaryotic.
- • Cells that do not have a nucleus and membrane organelles are called prokaryotic cells.
- • Cells that have a nucleus and organelles with membranes are called eukaryotic cells.
- • Some living things are unicellular and some are multicellular.
Nutrition
- • Living things have to be fed to meet their material and energy needs.
- • Organisms that can produce the nutrients they need on their own are called producers (autotrophs). For example, plants synthesize their own food.
- • Organisms that take their nutrients ready-made from the external environment are also called consumers (heterotrophs). For example, fungi and animals feed on heterotrophs.
Respiratory
- • Living things need energy to continue their vital activities.
- • This energy comes from the ATP (adenosine triphosphate) molecule.
- • Cells produce ATP by cellular respiration by breaking down food.
- • Respiratory reactions; There are three types of aerobic respiration, anaerobic respiration and fermentation.

Source: pixabay.com
Excretion
- • Excretion is the removal of waste materials formed as a result of the metabolic activities of living things from the cell or body.
- • Excretion takes place in different ways in living things.
Movement
- • Living things move for various reasons such as hunting, migration, reproduction, feeding their young, reaching light and water.
- • Unicellular organisms; It makes displacement movements with the help of structures such as whip, cilia and pseudofoot.
- • Movement is change of state in plants, mostly in the form of displacement in animals.
Response to Warnings
• Living things react to stimuli coming from the internal and external environment. This is important for living things to be in harmony with their environment and to continue their lives.
Metabolism
- • All the construction and destruction reactions in the organism are called metabolism.
- • Construction reactions in which simple molecules are combined to synthesize more complex molecules are called anabolism.
- • Chemical reactions in which large molecules are broken down into simpler compounds are called catabolism.
Homeostasis
- • The process of providing and maintaining a stable internal environment in the organism despite all environmental changes is called homeostasis. (inner balance)
- • All systems in living things work towards maintaining homeostasis.
- • For example; Adjusting the acid-base balance of body fluids, keeping the body temperature constant, throwing harmful wastes out of the body.

Source: pixabay.com
Adaptation
• Adaptation is all of the inherited traits that increase an organism’s chances of survival and reproduction in its environment. These traits are passed on from generation to generation.
Organization
- • In single-celled organisms, organization refers to the harmonious functioning of the structures within the cell.
- • Organization in multicellular organisms; consists of atoms, molecules, organelles, cells, tissues, organs, systems and organisms.
Reproductive
- • The creation of new individuals in order to continue the lineage of living things is called reproduction.
- • In asexual reproduction, the parent produces offspring with the same hereditary characteristics.
- Sexual reproduction is the formation of new individuals by the union of male and female reproductive cells. Offspring formed by sexual reproduction carry characteristics from both the mother and the father. In this way, genetic diversity is ensured.
Growth and development
- • Growth is achieved by an increase in the volume and mass of the cytoplasm in unicellular organisms and by an increase in the number and volume of cells in multicellular organisms.
- • Development is the functional maturation of the structures of the living thing by changing over time.