In this post, we will discuss the 10 characteristics of the circulatory system, including its functions, structure, and components.The circulatory system is one of the most important systems in the human body. It is responsible for the transportation of oxygen, nutrients, hormones, and other important substances to various parts of the body.
The circulatory system is a complex system of structures, organs and blood vessels. It is responsible for transporting and feeding nutrients from and to the cells and tissues throughout the body. In addition to transporting nutrients, the circulatory system transports oxygen throughout the body.
The circulatory system is composed of one of the main organs of the body, the heart. This organ is a muscle that pumps blood to nourish the rest of the body. This pumping work can be done thanks to nerve impulses.
The heart is an organ that functions uninterruptedly from the moment of conception (when it forms the embryo in the mother’s belly) until the moment of the death of the living being.
The circulatory system is the combination of the functioning of the cardiovascular system and the lymphatic system. The cardiovascular system is made up of the heart, blood vessels and blood; and the lymphatic system transports lymph unidirectionally to the heart.
Characteristics Of Circulatory System
1. General function
The general function of the circulatory system is to transport blood, which contains oxygen, nutrients, and other important substances, throughout the body. This allows various organs and tissues to receive the necessary resources to function properly. Additionally, the circulatory system plays a crucial role in removing waste products, such as carbon dioxide and urea, from the body. Overall, the circulatory system is responsible for maintaining the body’s internal environment and ensuring that all organs and tissues receive the necessary resources to function optimally.
2. Specific functions
In addition to the general function of transporting blood and maintaining the body’s internal environment, the circulatory system has several specific functions:
- Delivery of oxygen and nutrients: The circulatory system delivers oxygen and nutrients to all parts of the body, ensuring that cells have the energy and resources they need to function properly.
- Removal of waste products: The circulatory system removes waste products, such as carbon dioxide and urea, from the body, preventing them from accumulating and causing harm.
- Regulation of body temperature: The circulatory system helps to regulate body temperature by transporting heat away from the internal organs and to the skin’s surface, where it can be dissipated.
- Transport of hormones: The circulatory system transports hormones throughout the body, allowing them to regulate various bodily functions and maintain homeostasis.
- Defense against infection: The circulatory system includes white blood cells, which help to defend the body against infection by attacking and destroying foreign invaders, such as viruses and bacteria.
- Maintenance of pH balance: The circulatory system helps to maintain the body’s pH balance by transporting acids and bases to and from the lungs and kidneys, where they can be excreted.
- Maintenance of fluid balance: The circulatory system helps to maintain fluid balance in the body by transporting water and electrolytes to and from the kidneys, where they can be excreted.
- Transport of immune cells: The circulatory system transports immune cells, such as T cells and B cells, throughout the body, allowing them to identify and attack foreign invaders.
- Delivery of medication: The circulatory system can be used to deliver medication directly to specific parts of the body, such as the brain or heart, by using specialized drug delivery systems.
- Facilitation of blood clotting: The circulatory system helps to facilitate blood clotting, preventing excessive bleeding in the event of an injury.
3. The heart
The main organ of the circulatory system is the heart. This is located in the thoracic cavity. This is the body responsible for generating blood to reach the different organs of the body.
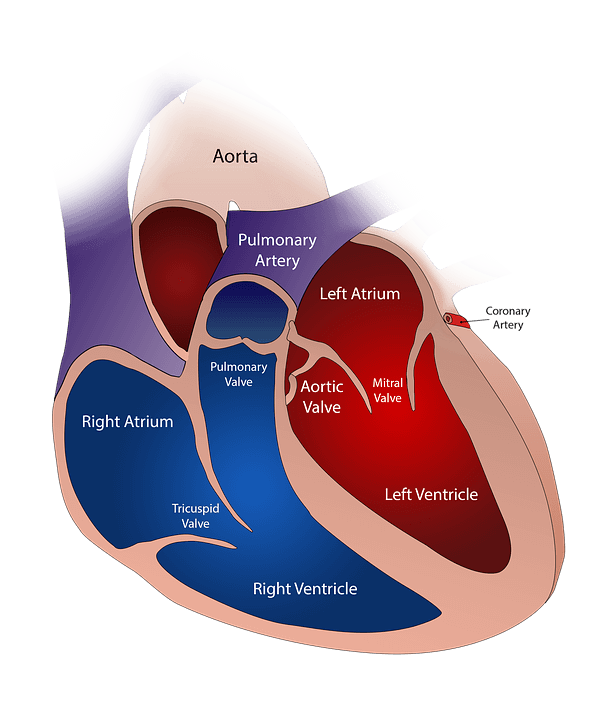
4. Pumping methods
The heart, may have two pumps or four. The first is known as an open system. This has two cameras, while the second is known as a closed system and has four cameras.
Respiratory system with heart of 2 cameras (open system). In this case the blood flows freely throughout the body but the oxygen is transported through tubes that open to the outside. Here is the circulatory system of insects and arachnids.
Respiratory system with heart of 4 cameras (closed system). In this case, the blood circulates through the blood vessels and this blood does not leave the vessels. Mammals, in general, have this type of closed system.
5. Blood vessels
Parts of the circulatory system.
Within the circulatory system are the blood vessels. These might be:
Veins. They are the blood vessels that carry blood back from the organs to the heart. This return lacks oxygen and nutrients.
Arteries They are the blood vessels that come from the heart loaded with oxygen to the different organs. This blood always has more pressure than that which circulates in the veins.
Capillaries They are tiny blood vessels of just 1 millimeter. In them an exchange takes place between the blood and the liquid that is in the cells of the tissues (called interstitial liquid). Oxygen passes through the capillary wall. This way it enters the organism (from the tissue to the blood) and the carbon dioxide comes out.
6. The blood
Blood is the vehicle through which oxygen and nutrients travel through blood vessels. To put it another way, blood is like the flow of a river. This is red in color and contains:
Red blood cells. They are the ones that transport oxygen from the lungs to the tissues.
Platelets. They are responsible for stopping bleeding and favor the coagulation of blood.
White blood cells They are responsible for defending the body from viruses and bacteria. In other words, they are the body’s defenses.
Plasma. Plasma serves as a transport of nutrients but is also, in itself, a substance that contains various proteins.
7. Lymphatic system
The lymphatic system produces and transports lymph from the tissues to the blood vessels. The lymphatic system is indispensable for the body’s immune system. The lymph is transported unidirectionally to the heart.
8. Circulatory system diseases
Arteriosclerosis
Myocardial infarction
Arterial hypertension
Arrhythmia
Hereditary or congenital diseases
Leukemia
Stroke
9. Risk factor’s
Sedentary
Smoking
Obesity
Hypercholesterolemia
Mellitus diabetes
Stress
10. The case of plants
Plants also have a circulatory system, but it differs from that of animals. The plant circulatory system is known as the vascular system, and it is responsible for transporting water, nutrients, and other substances throughout the plant.
The vascular system is composed of two types of vessels: xylem and phloem. Xylem vessels transport water and minerals from the roots to the rest of the plant, while phloem vessels transport organic compounds, such as sugars and amino acids, from the leaves to the rest of the plant.
The vascular system in plants is also involved in maintaining turgor pressure, which helps to keep the plant upright and enables it to maintain its shape. Additionally, the vascular system plays a role in defense against pathogens by transporting immune cells and other defense mechanisms throughout the plant.
Overall, the circulatory system in plants is essential for their growth and survival, allowing them to transport necessary resources and defend against pathogens.