What is gallbladder inflammation or its medical equivalent, Acute Cholecystitis? How do gallstones cause gallbladder inflammation? What are the symptoms?
Inflammation of the gallbladder as a result of any cause is called acute cholecystitis. In patients with acute inflammation of the gallbladder, the most common factor causing this is gallstones. However, there may be inflammation in patients who do not have stones in the gallbladder.
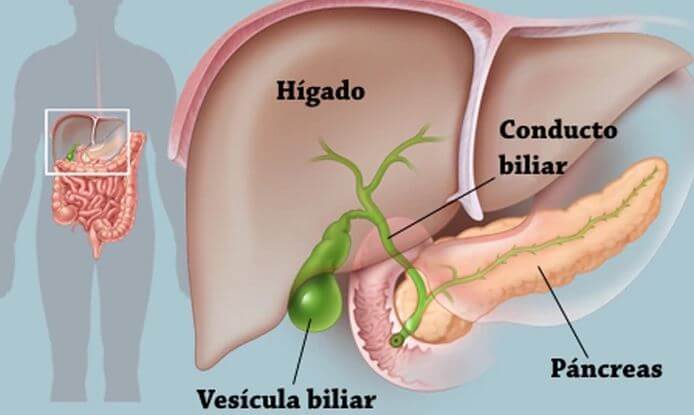
What is Gallbladder Inflammation?
In patients with acute inflammation of the gallbladder, the most common factor causing this is gallstones. However, there may be inflammation in patients who do not have stones in the gallbladder.
Although acute cholecystitis usually presents with sudden onset of abdominal pain, detailed examination and ultrasound imaging are very important since there are different diseases with these symptoms. Acute cholecystitis, which can occur due to any triggering or no reason, can lead to serious complications that can lead to death if not treated. For this reason, patients who experience symptoms of gallbladder inflammation should apply to health institutions as soon as possible and undergo an examination.
Why Do Gallbladder Stones Cause Gallbladder Inflammation?
The gallbladder is the storage organ of bile fluid, located just below the liver, that helps the body digest fats. Bile produced in the liver is stored in the gallbladder and transmitted to the small intestines through the ducts during the digestive process.
Inflammation of the gallbladder is called acute cholecystitis. The most common cause of acute cholecystitis is gallstones, called cholelithiasis. Although the exact cause of stone formation in the gallbladder is not known, it is a very common health problem in our country and in the world. Acute cholecystitis is most likely to occur when stones in the gallbladder block the ducts and block the flow of bile.
The vast majority of cholecystitis cases occur as a complication of stone formation in the gallbladder. Stones formed in the gallbladder block the bile ducts and cause inflammation in the gallbladder. Bile stasis (stopping of bile flow), which occurs as a result of the obstruction of the ducts by the stone, triggers the release of inflammatory enzymes, causing acute inflammation. 5-10% of acute cholecystitis cases develop as acute acalulous cholecystitis with inflammation without gallstones. In both cases, the treatment process should be started without losing time.
What are the Causes of Gallbladder Inflammation Apart from Gallbladder Stones?
Although rare, acute cholecystitis may develop due to different causes such as serious diseases, long-term malnutrition and tumors. Recurring episodes of cholecystitis indicate that cholecystitis has become chronic. When scientific studies are examined, it has been determined that gallbladder inflammation is much more common in women than in men. Again, although the cause is unknown, the incidence of acute cholecystitis seems to increase with age.
Therefore, advanced age constitutes a risk factor for developing this disease. The higher prevalence of the disease in Native Americans, Scandinavian countries and countries such as Spain brings with it the thought that genetic factors, environmental factors and dietary habits play a role in the development of the disease.
What are the Symptoms of Gallbladder Inflammation?
The most common symptom in acute cholecystitis is severe abdominal pain that starts suddenly and lasts for several hours. This pain is usually seen in the upper right part of the abdomen, but may radiate to the right shoulder or back. Abdominal pain from acute cholecystitis is often described as a sharp pain or dull cramps. Many people feel the need to go to the emergency services because the pain is unbearable. In addition to pain, some other symptoms seen in acute cholecystitis include:
- Clay-like light-colored stool
- Nausea and vomiting
- High fever
- Yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes (jaundice)
- Pain that increases after meals
- chills and shivering
- swelling in the abdomen
Individuals experiencing the above symptoms are more likely to have acute cholecystitis. For this reason, patients who experience one or more of these symptoms should apply to the emergency services without wasting time. If cholecystitis lasts for a long time or causes recurrent symptoms due to inflammation, it means that it turns into chronic cholecystitis.
How is Gallbladder Inflammation Diagnosed?
The first place of application for individuals experiencing acute cholecystitis is usually the emergency services. The primary reason for this is that it causes sudden and severe abdominal pain. However, since the symptoms of acute cholecystitis have similar characteristics with many different diseases, some diagnostic tests should be applied to diagnose the disease. First of all, a detailed medical history is taken from patients who apply to health institutions. In addition to information such as when the pain started, how its severity is felt, and how it was felt, some information such as the diseases found in the person and the drugs used are also obtained. A physical examination is usually done afterward.
With this examination performed by the physician, it is tried to determine the problematic area that causes pain by pressing on certain areas of the abdomen, and it is also checked whether there is any swelling in the abdomen. Physical examination has an important place in distinguishing other diseases that can cause severe abdominal pain, especially appendicitis. However, medical imaging techniques should be used for definitive diagnosis. The most common method for this is abdominal ultrasonography. In abdominal ultrasounds, sound waves are used to visualize the organs in the abdominal cavity. Another method that can be used in the diagnosis of cholecystitis is hepatobiliary scintigraphy.
With hepatobiliary scintigraphy, the upper part of the small intestine, liver, gallbladder and bile ducts can be visualized. In this way, problems related to these organs can be detected. With another diagnostic test called cholangiography, a dye is injected into these channels so that the gallbladder and its ducts can be visualized. Computed tomography (CT) scans, on the other hand, are an imaging technique that can be used in the diagnosis of liver and gallbladder diseases, as in all internal organs. In addition to medical imaging tests, some blood tests are often used. In this way, some blood tests such as liver enzymes, bilirubin, and hemogram are applied to investigate the signs of the disease. As a result, in patients diagnosed with acute cholecystitis, a treatment plan is determined and applications are started.
How is Gallbladder Inflammation Treated?
Patients with acute cholecystitis are usually hospitalized and kept under observation after diagnosis. Since the gallbladder is part of the digestive system, stopping oral feeding will help the gallbladder rest. Therefore, fluid and nutritional needs are met intravenously (through a vein) during the hospitalization period. In order to reduce the abdominal pain experienced and to fight infection, painkillers and antibiotics are usually recommended. In case of recurrence of cholecystitis, it is generally recommended by physicians to remove the gallbladder with the help of surgical operation. Today, with the developing medical technologies, these operations are performed laparoscopically (closed method) in suitable patients. However, in some patients, open operations may be required depending on the condition of the gallbladder and the anatomical structure of the patient. Surgery to remove the gallbladder is called cholecystectomy.
In humans, even without a gallbladder, food can be digested normally. In patients who have had their gallbladder removed, bile reaches the small intestine directly. However, in order for the body to get used to it, a low-fat diet should be applied for 2-3 months. Then, individuals who do not have additional diseases can switch to a normal diet. In addition to the treatment process, some measures can be taken against acute cholecystitis. Being overweight and obesity are risk factors for acute cholecystitis. For this reason, reaching the ideal weight of overweight individuals, applying a healthy and balanced diet program significantly reduces the risk of developing both acute and chronic cholecystitis.
Since rapid weight loss can also trigger gallbladder diseases, the slimming process should be continued consciously with personalized nutrition programs under the supervision of a dietitian. At the same time, in individuals with high cholesterol values, the possibility of developing cholecystitis can be reduced by diet and the use of cholesterol-lowering drugs, if recommended by the physician.