Information on the structure of the intestine. What are the functions of intestine and intestine diseases?
Intestine; the section of the alimentary canal that extends from the stomach to the anal opening. The human intestine is divided into two major portions: the small intestine, which is narrow and coiled, and the large intestine, which is wider and appears to consist of a series of pouches.
Source: pixabay.com
Structure:
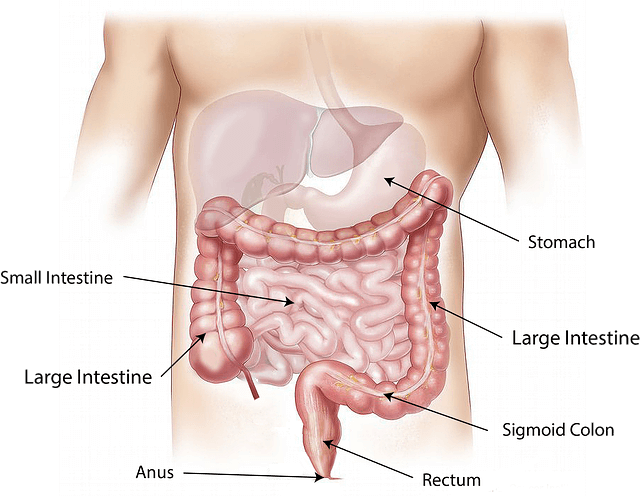
The small intestine is about 23 feet (7 meters) long and consists of three subdivisions. The first division, called the duodenum, leads from the stomach and is nearly 1 foot (30 cm) long. The second segment, the jejunum, is almost 9 feet (2.7 meters) long, and the third segment, the ileum, is slightly more than 13 feet (4 meters) long.
The large intestine is about 5 feet (1.5 meters) long and joins the ileum in the lower area of the abdomen. The first section of the large intestine is a large pouch, the cecum, from which a slender fingerlike projection, the vermiform appendix, extends. The portion of the large intestine between the cecum and the rectum is called the colon, and it is subdivided into four segments: ascending colon, transverse colon, descending colon, and sigmoid colon. The rectum is a tube 5 inches (13 cm) long that opens into the anal canal. The anal canal is the shortest section of the intestine, measuring only about 1 inch (2.5 cm) in length. The terminal opening of the anal canal is known as the anus.
Functions:
The small intestine is the major site of food digestion and absorption. When foods enter the small intestine, they are broken down into small molecules, which are then absorbed through the intestinal wall into the bloodstream and lymphatic system. When the food mass enters the large intestine, it contains very little usable material, and the major function of the large intestine is to absorb water and inorganic salts from the mass. From the large intestine, the mass is moved into the rectum and it is eliminated through the anal canal.
Diseases:
The intestines are subject to a wide variety of diseases and disorders. Among the most common of these conditions are appendicitis, ulcers, hemorrhoids, colitis, and benign and malignant tumors.