What is the effect of temperature differences in air? How does wind form, what causes the different kinds of weather?
The atmosphere gets most of its heat from the sun indirectly. Radiant energy from the sun passes through the air without warming it very much. When the radiant energy strikes the earth’ s surface, it is absorbed and changed into heat. As the sun shines on the soil, rocks, and water, they become warmer and warmer. But air is a very poor conductor of heat. So only the air close to the earth gets heat from its surface by conduction. The warm air is distributed through the lower layers of the atmosphere by convection currents.
When air is heated, it expands and becomes less dense. The cooler, denser air above sinks toward the earth and pushes the warmer, less dense air upward. This cooler air is then warmed by conduction from the earth’s surface and pushed upward by more cool air sinking from above. So all three methods of heat transfer-radiation, conduction, and convection-help warm the air around the earth.
Cool air that sinks toward the earth is also warmed in another way. The pressure on the air at any height is caused by the weight of all the air above. As air moves downward, there is more and more pressure on it. So the air is compressed as it sinks. Careful tests show that when air sinks 1000 feet, it is compressed enough to make it at least 5° F. warmer. if air is warmed by compression, you can guess what happens when it expands. it is cooled just as much by expansion as it is warmed by compression. Warm air that is pushed upward 1000 feet expands enough to be cooled at least 5° F.
The temperature of the air changes with the seasons, and it alsa changes from day to day or even from hour to hour. The earth’s surface is warmed only when the sun shines on it. At other times, it is losing he at faster than it is gaining heat. For this reason, the air is usually warmer during the daytime than it is at night. But when clouds come between the earth and the sun, they shut off same of the rays that warm the earth’s surface. In summer, there are more hours of daylight than of darkness. The sun’s rays alsa strike the earth’s surface more nearly vertically. These are two reasons why the air is warmer in summer than it is in winter.
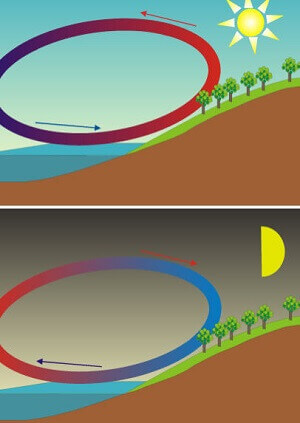
As you might expect, the air is warmest over places where the earth’s surface is warmest in the daytime, the air over land is usually warmer than the air over water. Soil and rocks are warmed very quickly, because nearly all of the radiant energy is absorbed and changed into heat near their surface. But a lake or an ocean is warmed much more slowly, because the heat is distributed through a much larger volume of water. Also, water reflects more radiant energy than soil and rocks do. At night, the air over water is often warmer than the air over land. Soil and rocks cool off faster than water, because nearly all of their heat is close to the surface. Theyare also much better conductors of he at than water is. Other changes in the temperature of the air are brought about by changes in the wind.

There is a slight wind in every room that is heated by a fireplace, stove, register, or radiator. Each one sets up a convection current in the room. The air moves because it is warmer at one place and cooler at another. Gravity pulls down harder on the cooler, denser air than on the warmer, less dense air. So the cooler air sinks, Hows along the floor, and pushes the warmer air sideways and upward. When air moves like this along the earth’s surface, we call the moving air a wind. A wind is really just a huge convection current. Some convection currents in the atmosphere extend only a few miles, while others extend thousands of miles.
Many changes in the direction of the wind are caused by changes in the temperature of the air at two places near each other. Suppose that you liye on the shore of a lake or the ocean. During the daytime, the air over water is usually cooler than the air over land. If the difference in temperature is great enough, the cooler air will push the warmer air sideways and upward. Then there will be a lake breeze or a sea breeze blowing toward the land. At night, the air over land is usually cooler than the air over water. So just the opposite of ten happens. A breeze blows from the cooler land toward the warmer water.
There are many other conditions that cause winds. The air over forests is cooler than the air over grasslands, while the air over grasslands is cooler than the air over plowed fields. When such places are close together, a difference in the temperature of the air produces light winds. These affect only small areas and bring about changes in temperature for just a few miles. On a hot summer day, a breeze blowing from Lake Michigan may lower the temperature in Chicago 20° F. Yet, 10 miles inland, the temperature may not change at all.
The wind and the temperature at any place are closely related. A change in one usually produces a change in the other. if the wind brings warm or cool air, the temperature goes up or down. if the temperature goes up or down, the direction and speed of the wind change. However, changes in the weather over large areas are not caused by local conditions. Huge masses of air moving across our country bring about changes in the direction and speed of the wind over large areas. Yet even these huge masses of air are affected by differences in temperature.
Near the equator, the air is always much warmer than it is at the North Pole or the South Pole. So the cold, dense air at the poles tends to sink and flow toward the warm regions near the equator. However, the rotation of the earth changes the direction of these air movements. The picture on this page shows how winds are affected by the earth’ s rotation.