ACTINOMYCOSIS, is an infectious disease affecting cattle and humans, more frequently men.
It is characterized by skin lesions and abscesses that may drain pus through long tracts (sinuses) and by woody swellings. The disease usually affects the face and neck, chest, or abdomen.
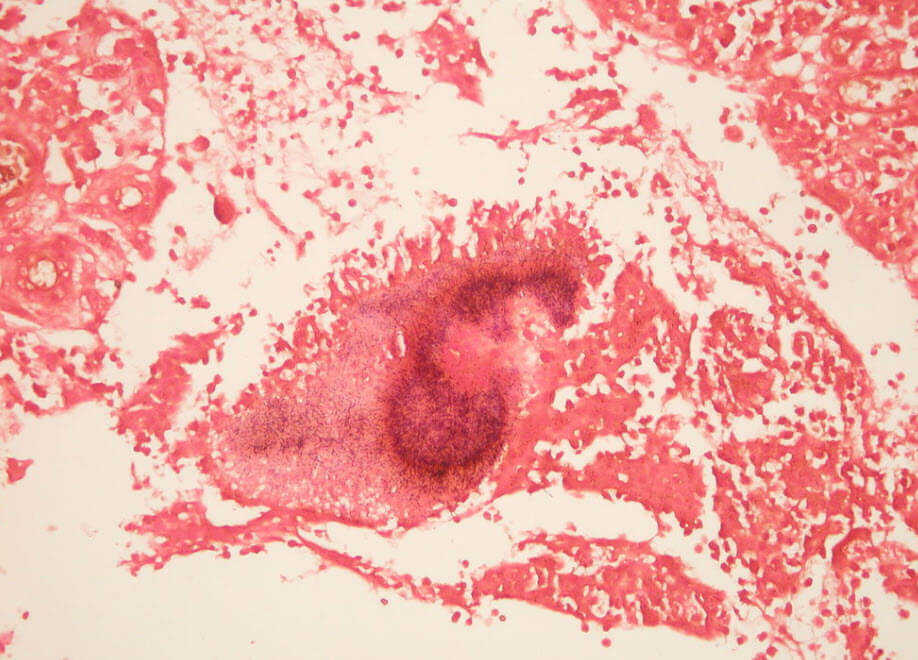
Actinomycosis Gram stain (Source : wikipedia.org)
Description.
Actinomycosis in the face and neck, also called cervicofacial actinomycosis, accounts for about 60 percent of all cases of the disease. The gums, mouth, tongue, pharynx, larynx, and ncck may become discolored, swollen, and uneven. The appearance of the disease is sometimes known and well-described as “lumpy jaw.” It is the least severe form of the disease, although in some cases it may affect the brain and the membranes surrounding the brain.
Actinomycosis in the chest, the most serious form of the disease, usually begins at the bronchial root of the lung and extends to the esophagus and to the membranes enveloping the lungs and heart. Often mistaken for tuberculosis, actinomycosis of the chest accounts for about 25 percent of all the cases of this infection. A cough, bloody sputum, pain in the chest that becomes worse with breathing, and a draining skin lesion are the chief symptoms.
Actinomycosis in the abdomen often begins in the appendix and spreads to the liver and spleen. Inflammation of the kidneys, bladder, and rectum can also occur. Abdominal pain, a palpable mass in the abdomen, and a draining skin lesion are the common symptoms.
In all forms of actinomycosis, fever, night sweats, chills, weight loss, pallor, and weakness may occur.
Cause.
In cattle, actinomycosis is caused by the fungus Actinomyces bovis; in humans, by A. israeli. The fungus may be present normally in the mouth, tonsils, and gastrointestinal tract and cause disease only when it invades nearby tissue in persons with low resistance. The fungus is found in the pus and tissue of the abscesses as small yellowish granules, termed “sulfur granules.”
Treatment.
The treatment of actinomycosis is twofold: the incision and drainage of the lesions and abscesses and the administration of antimicrobial drugs. Penicillin has been found to be the most effective drug. Almost all treated patients survive.