ACNE, is a disorder of the sebaceous (oil-secreting) glands of the face, chest, and back that usually occurs at the onset of adolescence.
The disorder is manifested by the appearance of blackheads, papules, and cysts.
Description.
The common type of acne, acne vulgaris, usually occurs on adolescents between the ages of 12 and 18. The skin becomes very oily, and blemishes start to appear. The first lesion to appear is usually a blackhead that blocks the normal flow of oil. Some blackheads develop into inflamed papules, which may become infected with bacteria on the surface of the skin and form infected lesions. In severe cases, several lesions may coalesce to form a cyst. If the lesions persist, they often burrow deeper into the skin, and permanent scarring may occur. A severe case of acne and the resultant scarring often causes the adolescent to become very shy and introverted. By age 16, many young people recover spontaneously, but the disorder sometimes persists and becomes progressively worse.
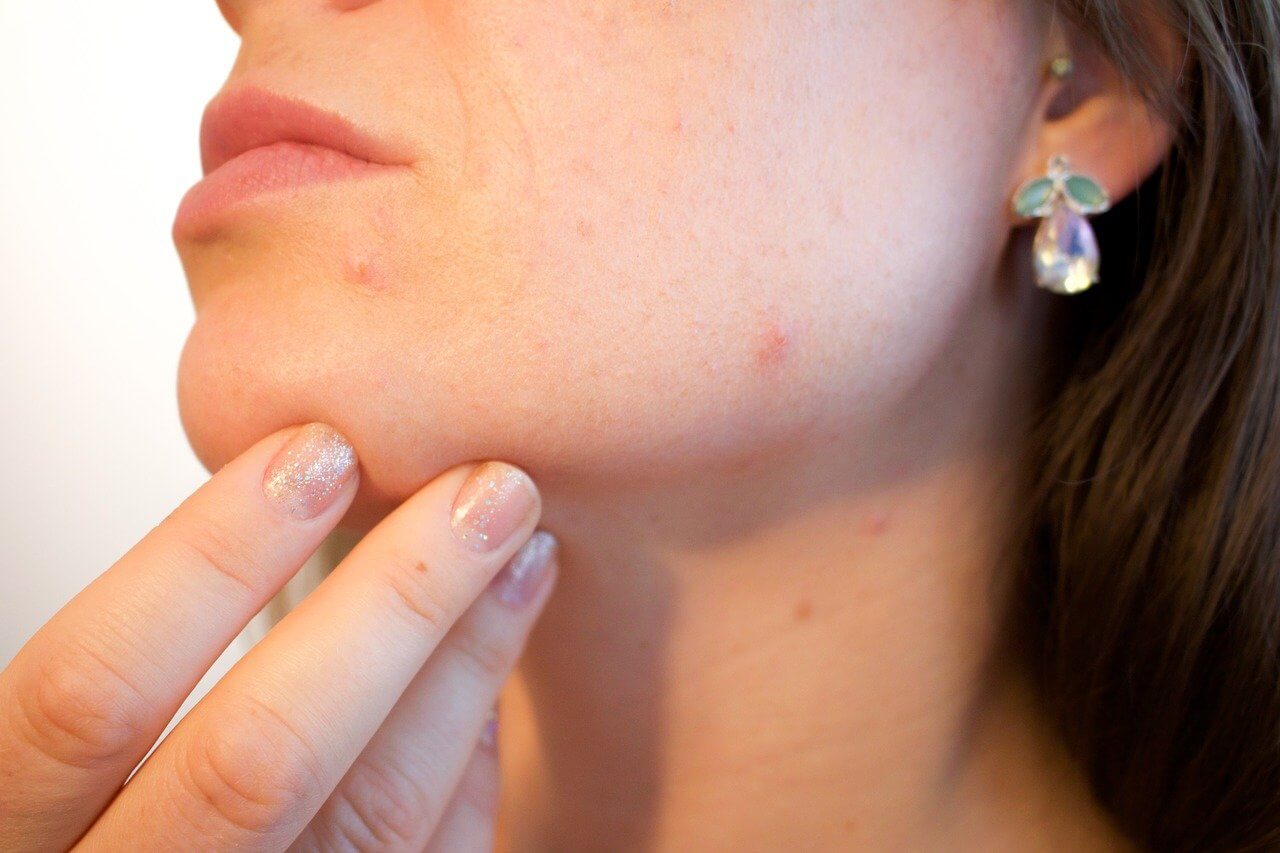
Source : pixabay.com
Middle-aged people are sometimes afflicted with a chronic disorder known as rosacea or acne rosacea, which resembles acne. Red blotches and pustular acnelike lesions (but no blackheads) appear usually on the cheeks and nose. The exact cause of the condition is unknown, but alcoholic beverages, tea, coffee, and spicy foods tend to aggravate the disorder.
Cause.
The basic cause of acne vulgaris is an endocrine imbalance. The predominance of the condition in adolescents, its tendeney to become worse at the time of the menstrual period, and its tendeney to end spontaneously alî point to an endocrine factor. At adolescence the secretion of the sex hormones—estrogen in the female and androgen in the male—becomes activated and causes an inerease in the secretions of the sebaceous glands.
Contributing Factors.
Acne vulgaris is often aggravated by such factors as poor nutrition, fatigue, and irregular elimination habits, emotional upsets, and poor skin hygiene. Diet plays such an important role in some cases of acne that a food allergy is sometimes thought responsible for the lesions. Emotional upsets often trigger an eruption of acne lesions. This can be seen in adolescents at examination times or during predate tension. Lack of exercise and infrequent exposure to sunlight often cause acne eruptions to become worse during winter months.
PREVENTION AND TREATMENT
Diet.
Acne sufferers should take special care to have a balanced diet, containing meat, fish, vegetables, green salads, and fruit. Chocolate, nuts, iodized salt, shellfish, cola drinks, pizza pies, frankfurters, fried foods, and rich desserts should be avoided.

Source : pixabay.com
Hygiene.
Acne is aggravated by failure to keep elean the areas affected with excessive oiliness or blemishes. Squeezing and picking the blackheads and pimples also worsens the condition. The face should be washed frequently with an antiseptic soap containing hexachlorophene. An abrasive soap may also be used to peel the skin. An antiseptic lotion containing alcohol and hexachlorophene is sometimes used to reduce the oiliness of the face. The sealp should be shampooed once a week or more frequently if needed.
Medical Treatment.
A therapeutic cream that contains sulfur, salieylic acid, and resorcinol is considered helpful in releasing blackheads and in drying the skin. A formula that contains benzoyl peroxide and hydroxyquinoline is reported to have a uniformly favorable response, but there is some incidence of side effects, such as excessive dryness and peeling of the skin. Another preparation that has been used experimentally contains Neomedrol®, neomyein, and sulfur and aluminum astringent. These preparations containing benzoyl peroxide or Neomedrol® are probably the most effective advance in the treatment of acne since the 1940’s.
The internal use of vitamin A and antibiotics such as sulfonamides and tetracycline helps in the reduetion of infection and may prevent the appearance of new lesions. Hormones should be administered to adolescents with great care, but for some girls, especially when the acne worsens at the time of the menstrual period, small doses of estrogen may be helpful. Small doses of thyroxine are also sometimes beneficial.
Ultraviolet Light and X-Rays.
Ultraviolet light, either natural or artifîcial, stimulates the skin to normal repair and growth, often by causing mild peeling. Peeling of the skin probably accounts for the frequent improvement of acne in the summer months.
Superfieial X-ray treatment is helpful in severe cases of acne where cysts have formed. The treatment itself does not cause scarring if performed by a qualified dermatologist.
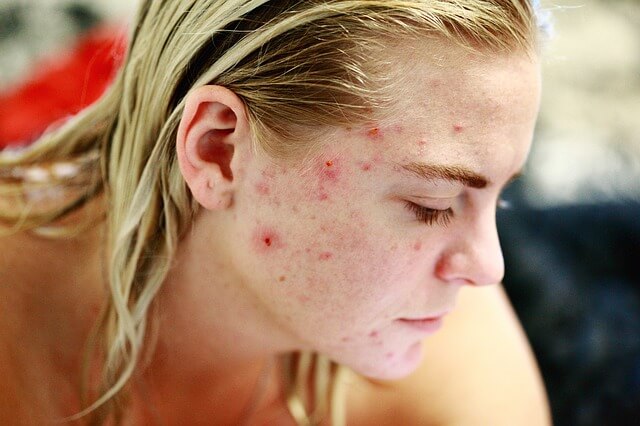
Source : pixabay.com
Surgery.
To remove the acne scars, a surgical procedure, called dermabrasion or surgical planing, is used to pare down the deep-pitted scars and make them less conspicuous. This process consists of freezing the skin with ethyl chloride after it has been cleansed with ethyl chloride. Next, a high-speed rotary brush is used to remove the superfieial layers of the skin. Then neomyein cortisone ointment is applied, and the treated skin is bandaged. An antibiotic is given internally to reduce the possibility of infection. The bandage is removed after two days, and the skin is completely regenerated in several weeks.
Chemical Peeling.
A procedure known as chemexfoliation or ehemerasure uses phenol (carbolic acid) or trichloracetic acid (25-35 percent) to peel the superfieial layers of the skin. This procedure is not so effective as dermabrasion, however.